

The three types of van der Waals forces include: 1) dispersion (weak), 2) dipole-dipole (medium), and 3) hydrogen (strong). Covalent compounds exhibit van der Waals intermolecular forces that form bonds of various strengths with other covalent compounds.
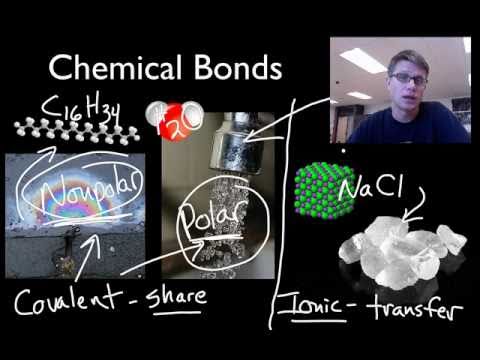
Ionic compounds exhibit electrostatic intermolecular forces that form strong bonds with other ionic species.They are grouped into 3 subcategories based on the type of intramolecular bonds that form a compound: Intermolecular forces are described below. Typically, these forcesbetween molecules form much weaker bonds than those bonds that form compounds. Intermolecular forces are the forces that attract molecules or particles to like or unlike molecules or particles. Metallic Bond: a bond resulting from the attraction between positive ions and surrounding mobile electrons. The electron donor (cation) now carries a net positive charge, and the electron acceptor (anion) now carries a net negative charge. The electron(s) involved in bonding is (are) transferred from the less electronegative to the more electronegative atom(s) forming ions. Ionic compounds are formed between atoms that differ significantly in electronegativity. Ionic Bond: a bond that holds atoms together in a compound the electrostatic attraction between charged ions. Network: compounds in which each atom is covalently-bonded to all its nearest neighbors so that the entire crystal is one molecule.Macromolecular compounds are high molecular mass compounds that are covalently-bonded and linear, branched, or cross linked.Molecular compounds refer to covalently-bonded species, generally of low molecular mass.There are 3 types of intramolecular bonds: covalent, ionic, and metallic.Ĭovalent Bond: a bond in which a pair or pairs of electrons is shared by two atoms. Intramolecular bonds are the bonds that link together atoms to form compounds. Several types of chemical bonds exist, and can be classified based on the atoms involved and the distribution of electrons between the atoms. Chemical bonds are defined by the attractive forces between their nuclei and electrons, and can vary in range from only passing attraction to irreversible binding. Chemical bonds are formed when the interaction between two or more atoms requires less energy than maintaining the atoms separately.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
